Drivetrain approach with example (minimizing spread of COVID-19 across students of a department)
Table of contents:
What is the Drivetrain approach ?
It is basicly a process to design data products, to ensure that your modeling work is useful in practise. It was introduced in 2012 by Jeremy, along with Margit Zwemer and Mike Loukides. You can find out more about it here: Designing good data products
Ok, but what does it consist of ?
Well, now that we saw what it was usefull for, and where it came from, let’s see the four steps that compose it 1.
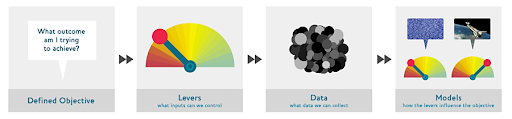
- We need to define the objective (the end goal)
- Next we need to identify the levers (what can we control)
- After that collect relevent data
- Finally train our model
Example
No good explanation is made without a concrete example, so let’s do that.
Let’s say i’am a director of the computer science department. And i want to minimize the spread of COVID-19 across students of my department (this is the objective).
One of the things i can controll, is to make sure everyone is wearing a face mask, by installing for example cameras across the department entries that would detect if you are wearing a mask or not and would let you or not enter by say opening the door or locking it (this is the lever).
Now to make such a system, i’ll need to train a model for image recognition, so i’ll collect data which will consist of people wearing masks and others not (that’s the data phase).
Finally come the ‘fun’ part where you actually train your model and get to see it in action.
Reference
-
This blog post was highly influenced by the book Deep Learning for Coders with fastai & PyTorch, in fact i’am writing this blog as part of the homework.
If there is any problem of copyright regarding the use of the picture or anything else please let me know. ↩